In a significant move, the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024, has been referred to a joint parliamentary committee (JPC) for detailed scrutiny. The decision was announced on August 8, 2024, following a heated debate in the Lok Sabha. The committee, comprising 21 members from both houses of Parliament, will review the proposed amendments and provide recommendations.
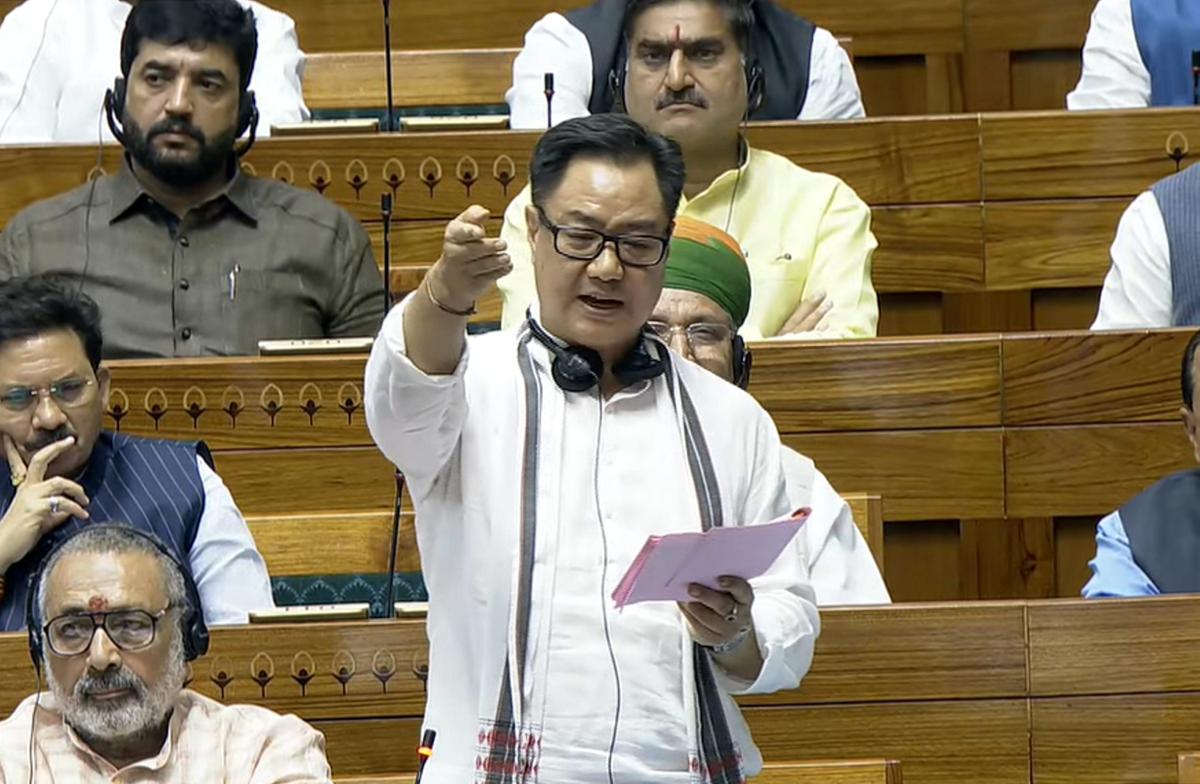

Background of the Waqf Amendment Bill in Parliament
The Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024, introduced by Union Minority Affairs Minister Kiren Rijiju, aims to bring reforms to the administration of Waqf properties. The bill proposes significant changes, including the introduction of the District Collector as an arbiter to decide whether a property is Waqf or government land. The bill has faced strong opposition, with critics labeling it “draconian” and an attack on the Constitution.
Formation of the Joint Committee
Speaker Om Birla announced the formation of the joint parliamentary committee after consulting leaders from all parties. The committee will consist of 21 members, with 20 from the Lok Sabha and 10 from the Rajya Sabha. This move is seen as an effort to ensure thorough examination and bipartisan consensus on the bill.
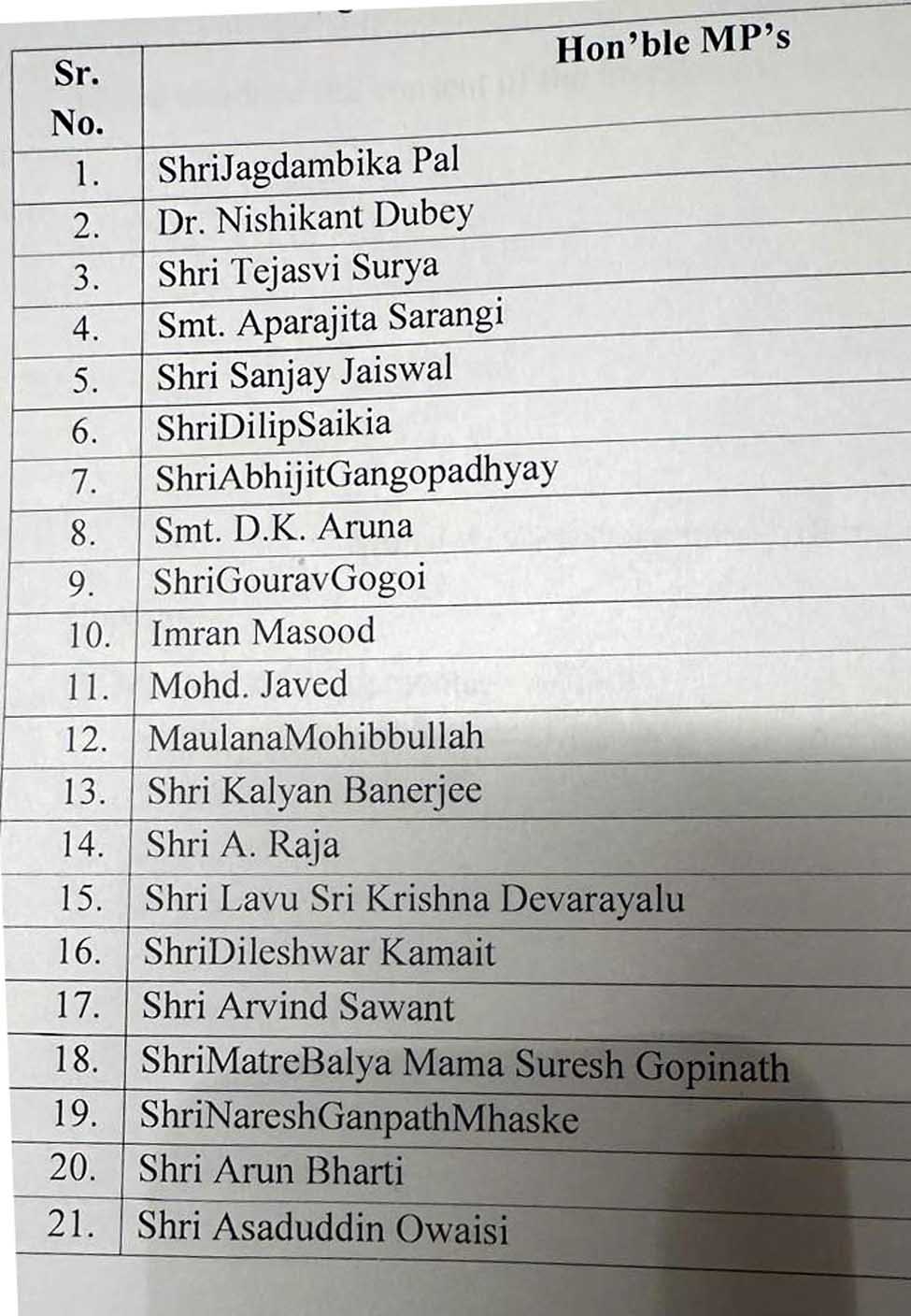
Objectives of the Committee
The primary objective of the joint committee is to scrutinize the provisions of the Waqf (Amendment) Bill and address concerns raised by various stakeholders. The committee will hold meetings, invite expert opinions, and consider suggestions from the public to ensure that the bill is comprehensive and balanced.
Political Reactions
The decision to refer the bill to a joint committee has elicited mixed reactions. The ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and its allies, such as the Janata Dal (United) and the Telugu Desam Party, have supported the move, emphasizing the need for transparency and reform in the Waqf administration. However, opposition parties, including the Congress, have expressed reservations, arguing that the bill could undermine the autonomy of Waqf Boards and interfere with religious matters.

Key Provisions of the Bill
The Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024, includes several key provisions aimed at improving the management of Waqf properties:
- District Collector as Arbiter: The bill proposes that the District Collector will have the authority to determine whether a property is Waqf or government land, replacing the current system where the Waqf Board has this power.
- Preliminary Survey: A detailed process for the preliminary survey of properties by the District Magistrate is introduced, ensuring a more transparent and accountable system.
- Reforms in Waqf Boards: The bill seeks to implement reforms suggested by previous committees to address issues of corruption and mismanagement within Waqf Boards1.
Next Steps
The joint parliamentary committee will begin its review process immediately, with the aim of presenting its report in the upcoming session of Parliament. The committee’s findings and recommendations will play a crucial role in shaping the final version of the bill.
Conclusion
The referral of the Waqf (Amendment) Bill to a joint parliamentary committee marks a significant step in the legislative process. It reflects the government’s commitment to ensuring thorough scrutiny and bipartisan support for important reforms. As the committee begins its work, all eyes will be on its deliberations and the impact they will have on the future of Waqf administration in India.
For More News updates, Follow Read Now News
